Choice Hotels – Value Investing Price Points
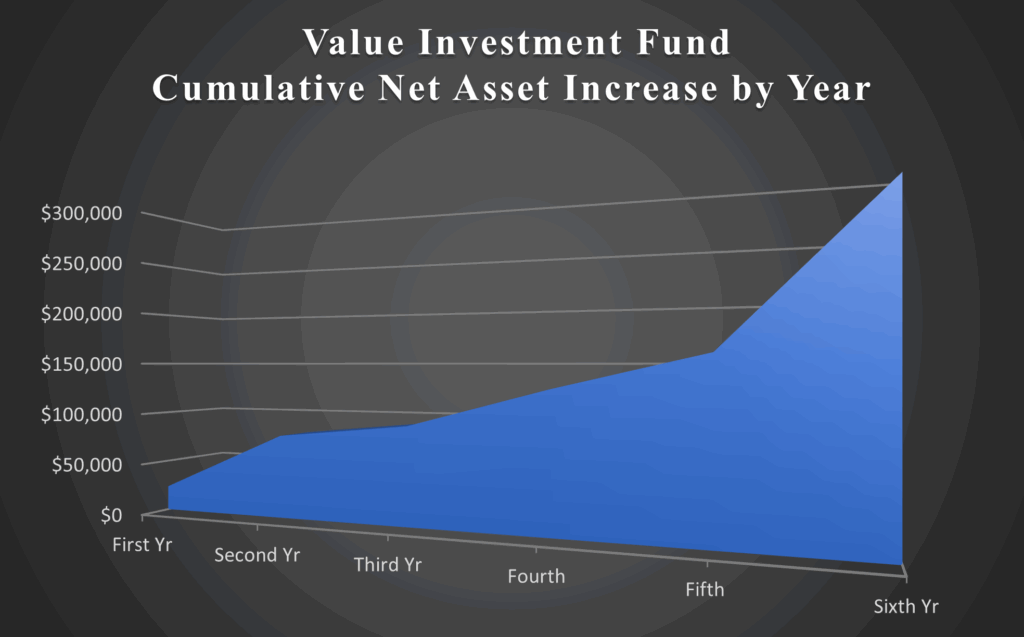
Choice Hotels – Value Investing Price Points Choice Hotels is one of the six potential Value Investment Fund members within the Hotels Industry pool of investments. There are four standard value investing price points for the reader to consider, along with three key performance indicators. A value investor takes into consideration all of these price […]
Choice Hotels – Value Investing Price Points Read More »